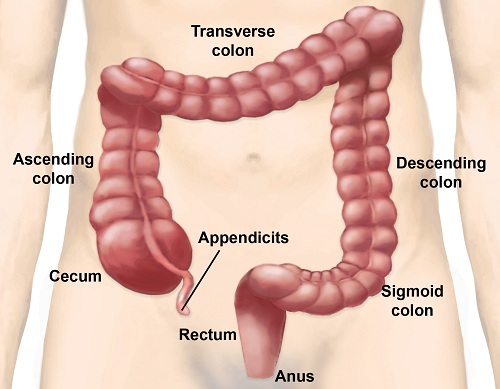
|
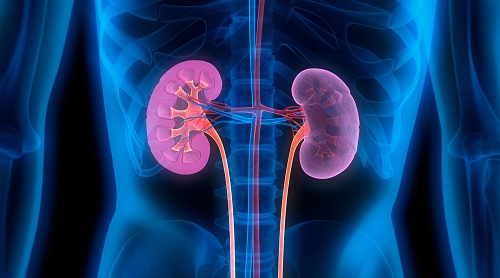
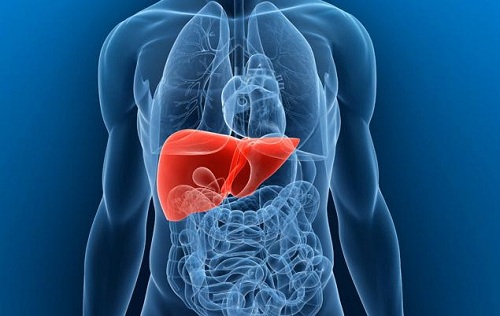
The excretory system is essential to one’s health. Its responsibility is to remove waste from the body. The excretory system is made up of numerous organs that work in unison to ensure that waste is effectively removed from your body. Below are the details of the organs of excretory system, along with the roles they play in detoxification. Primary Excretory System Organs 1. KidneysKidneys are bean-shaped organs of a reddish brown color that are found in the sides of the vertebral column. Once the body has extracted what it
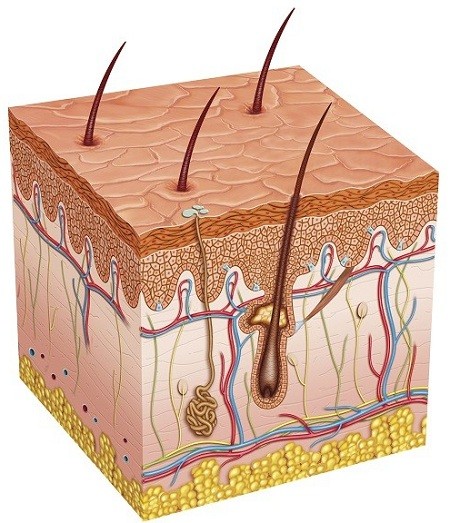
The skin performs its excretory function via the sweat glands. These glands produce sweat that contains salt, excess oils, water, and other unnecessary substances which are then excreted out of the body through small pores. Sweating also helps to cool the body during evaporation. 3. Lungs
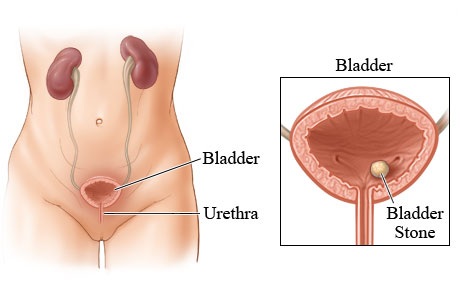
The waste fluid that is created in the liver and collected in the kidney is transferred into the urinary bladder where it is temporarily stored until the individual urinates. The urinary bladder provides a short term solution for storing urine in the body until it is ultimately discharged.
The ureters tubes of smooth muscle fiber transfer liquid waste from the kidneys into the urinary bladder. The urine is moved with peristaltic movements which force the urine away from the kidneys. The ureters also have ureterovesical valves which ensure the waste fluid does not travel back into the kidney. 5. UrethraThe urethra runs through the penis in males, and serves as a carrier of semen as well as urine for their ultimate Food particles are absorbed into the blood stream via the small intestine. The undigested substances
Kidney stones are believed to form from crystals that have separated from urine, forming hard masses in the urinary tract, though the exact cause is unknown. Symptoms for kidney stones include extreme pain, cramping in the lower abdominals and back, nausea, and vomiting. Most kidney stones can be passed by increasing your intake of water to flush them out, although surgery may be needed in some cases. 2. UrethritisUrethritis is a viral or bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the urethra. Symptoms for urethritis vary between the sexes. Symptoms for men include pain or swelling of the penis, blood in urine or semen, frequent urination and pain during ejaculation. Symptoms for females include pain during urination, abdominal pain, fever, chills, frequent urination, vaginal discharge and pelvis pain. Urethritis is usually treated with anti-viral medication, or antibiotics. Painkillers are often used to help sufferers combat the symptoms. 3. PyelonephritisPyelonephritis is a type of urinary tract infection that travels from the urethra or bladder and to the kidneys. This infection occurs when bacteria enter the body through the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent urination, burning during urination, blood in the urine, pain in the groin and abdominal pain. Pyelonephritis is usually treated with oral anti-biotics, although the anti-biotics are sometimes administered intravenously in cases of severe infections. 4. CystitisCystitis is the medical term for inflammation of the bladder and it is one of the most common disease that affects excretory system organs. As the bladder stores urine before it is excreted from the body, bacteria can build up in the bladder and cause cystitis. 5. Urinary Tract InfectionUrinary tract infection (UTI) is the infection of the urethra or the bladder. The symptoms include abdominal pain, painful or difficult urination and fever. The best way to avoid UTI is by drinking loads of water. (责任编辑:) |

.jpg)
.jpg)